

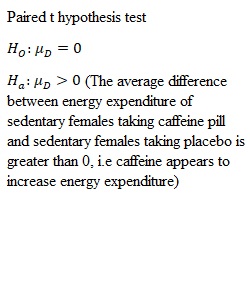
Q Purpose In this assignment you will practice using a p-value for a hypothesis test. Recall that a p-value is the probability of achieving the result seen under the assumption that the null hypothesis is true. Using p-values is a common method for hypothesis testing and scientific and sociological studies often report the conclusion of their studies using p-values. It is important to understand the meaning of a p-value in order to make proper conclusions regarding the statistical test. Task Since its removal from the banned substances list in 2004 by the World Anti-Doping Agency, caffeine has been used by athletes with the expectancy that it enhances their workout and performance. However, few studies look at the role caffeine plays in sedentary females. Researchers at the University of Western Australia conducted a test in which they determined the rate of energy expenditure (kilojoules) on 10 healthy, sedentary females who were nonregular caffeine users. Each female was randomly assigned either a placebo or caffeine pill (6mg/kg) 60 minutes prior to exercise. The subject rode an exercise bike for 15 minutes at 65% of their maximum heart rate, and the energy expenditure was measured. The process was repeated on a separate day for the remaining treatment. The mean difference in energy expenditure (caffeine – placebo) was 18kJ with a standard deviation of 19kJ. If we assume that the differences follow a normal distribution can it be concluded that that caffeine appears to increase energy expenditure? Use a 0.001 level of significance. a) (6pts)State the null and alternative hypothesis in symbols. Give a sentence describing the alternative hypotheses
Q b) (4pts)Check the requirements of the hypothesis testc) (3pts)Calculate the test statisticd) (3pts)Calculate the p-value
View Related Questions